AI is the biggest technological breakthrough of the 21st century
Whether you know it or not, Artificial Intelligence has impacted you and I in our daily lives.
It has become a staple in today’s society, from looking up something on the web, to speaking to a virtual assistant, to playing video games and talking to chatbots, just to name a few.
AI is so ubiquitous that its huge impact on our lives is undeniable.
Its ability to analyse vast amounts of data inconceivable to humans has allowed for smarter, more helpful devices that are assisting us in ways once thought impossible.
For those who don’t yet know what AI is, it’s a computer system that allows for the ability of a machine to display human intelligence, such as speech-recognition, problem-solving and language translation.
It does this by receiving data or input, such as through sensors, and then analyses and perceives the information to perform the most desirable action.
Say, for example, an autonomous car. It has radar sensors that can monitor cars nearby, and using this data it can automatically stop or move depending on the distance of a nearby vehicle. It also has video cameras that can detect traffic lights, look for pedestrians and read road signs in order to act accordingly.
The term ‘Artificial Intelligence’ was first coined in 1955 by John McCarthy. The first working AI programs were written before that, in 1951, designed to play checkers and chess.
Since then, numerous well-known films have labelled AI as a terrifying manipulative machine or a human-killing robot whose goal is to take over the Earth.


That stage still hasn’t been reached, but with advances in machine learning (AI’s ability to learn for itself), who knows?
Over the years, AI has made significant advances and reached many milestones. Who can forget the time when the then unbeatable, World Chess Champion Garry Kasparov, arguably the greatest chess player ever, lost to IBM’s super computer Deep Blue in 1997.

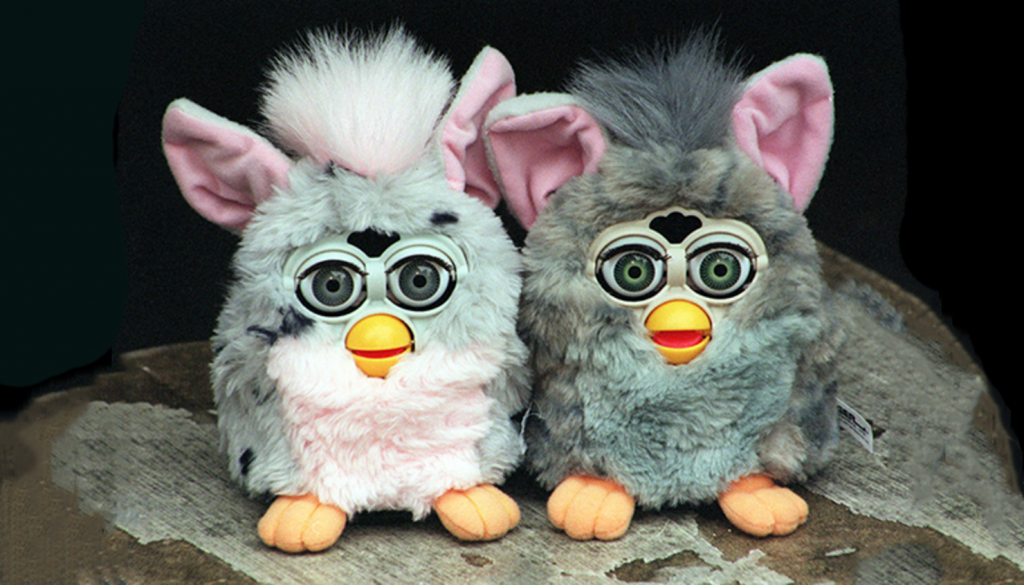
In 1998, Furbies hit shelves in time for Christmas. These furry, artificially intelligent toys learnt language over time the more you spoke to them, using machine learning. It was the first attempt to introduce artificially intelligent toys into the domestic world.

In the 21st century, AI has come a long way, shifting from the ‘test’ phase to something that impacts us every single day, directly and indirectly.
It is, judging by its incomparably abundant use paired with its unfathomable potential, the biggest technological breakthrough of the 21st century.
Yes, there are drones, VR, AR, robots, blockchain technology, but AI has a much wider scope of usage, and in fact, it can power many of these aforementioned technologies to make them even better.
That is why AI is a game-changer, it has limitless opportunities to make so many devices smarter. Drones have become autonomous because of AI and robots use AI to converse with others and make facial expressions.
It’s like if you asked somebody a hundred years ago where electricity could be used, it can be used everywhere!
Now to open your eyes to the impact that AI has on today’s society, here are some examples of ways you may or may not have known AI is being used today
1. Online shopping and advertising
Artificial intelligence is widely used in online shopping sites to recommend products personalised for you.
Have you ever looked something up on the internet and then creepily discovered that an online shopping site has recommended the product or advertised a similar product you just looked up? Well, AI did that.
It takes into account not only your web searches but also your previous purchases and other online activity.
It is used to increase the time spent on a website and also to boost the amount of clicks and advertisement gets.
These sorts of recommendation systems are also used by entertainment services such as Netflix to show movies that you are most likely to watch.
2. Web search
Search engines, such as Google and Bing, take into account a vast input of data to provide the most relevant search results possible.
Both of these search engines also use machine learning to understand more about the user and feed personalised results.
Interestingly, Pinterest, the popular image sharing site uses deep learning to learn more about the intents behind users’ searches and surface personalised results for each user. For example, if you search ‘diy kitchen cabinets’, it returns results ranging from ‘how to build your own cabinets’ to ‘before and after kitchen transformations’. After you click on several results that match your search, Pinterest will understand your intent and your search results will narrow.
3. Digital personal assistants, such as Siri and Alexa
Digital personal assistants use several different examples of AI.
Understanding speech, which we humans take for granted, was quite a tough ask for a machine. But using Natural Language Processing (NLP), Siri and Alexa are able to decipher what we say from a range of languages.
In natural language processing, a person’s voice is picked up via a microphone and has to be separated into fragments of data to understand the grammatical structure of sentences.
It is a sophisticated process with a lot of different combinations of data to take into account, but one that AI handles extremely well today. It isn’t often that Siri or the Google Assistant misunderstands my speech, although some complex words can be misinterpreted.
Digital personal assistants such as Siri and Alexa also utilise machine learning to constantly fix some of its errors. For example, if you ask Siri or Alexa a request that comes up with an error, they can take this data and try to fix it for the next time.
If the response was favourable, they’ll also take this into account. I’ve had several times where the Google Assistant has asked me if its response to my query was good. This is machine learning coming into play, as the Google Assistant is using my answer to improve or keep its response.
4. Smart thermostats such as Nest
Smart thermostats such as the popular Nest uses AI behavioural algorithms to understand the user’s heating and cooling patterns in order to anticipate when and by how much the user would like to change the temperature, thus doing so automatically.
It also enables energy to be saved as it turns off once the suitable temperature has been reached.
5. Autonomous cars
Yes, self-driving cars are not yet in the mainstream market, but it’s a symbol of the potential that AI holds to make devices smarter and also our lives easier.
Google-owned Waymo is one company driving into the autonomous car industry. In fact, in November of 2019, Waymo One was the first autonomous service worldwide operating without any safety drivers in the car.
The future of AI
AI still has a long road ahead and the potential to grow smarter every day. You could even consider AI to be in its infancy, with machine learning still in its early stages. With machine learning, minimal human intervention would be needed, as it learns on its own. That would make devices more efficient, and our lives and jobs much easier.
Those examples of AI mentioned above are only a tiny part of the abundant capabilities Artificial Intelligence holds.
It has the potential to revolutionise healthcare by identifying illnesses and making diagnosis more efficiently and accurately compared to humans. For example, some are considering its use in evaluating CT scans and electrocardiograms.
Some promising examples of AI’s use in healthcare includes Microsoft’s Hanover, which assists doctors in choosing the right cancer treatment from among the more than 800 medicines and vaccines.
AI was also able to diagnose eye conditions within 30 seconds and recommend treatment with more than 95% accuracy.
The cybersecurity industry is also set to be drastically changed by the introduction of AI. It’s being used to automatically detect malicious activity and by using machine learning, it can learn to detect cybersecurity threats faster and more efficiently.
AI is also being experimented to become a tool to spot poverty around the world. In 2016, Stanford University economist Marshall Burke used AI to analyse satellite imagery to find potential spots where poverty is occurring.
The AI found features that related to poverty which ‘were patterns to the eye that don’t look like anything we recognize, but they’re patterns that the model found useful,’ according to Burke.
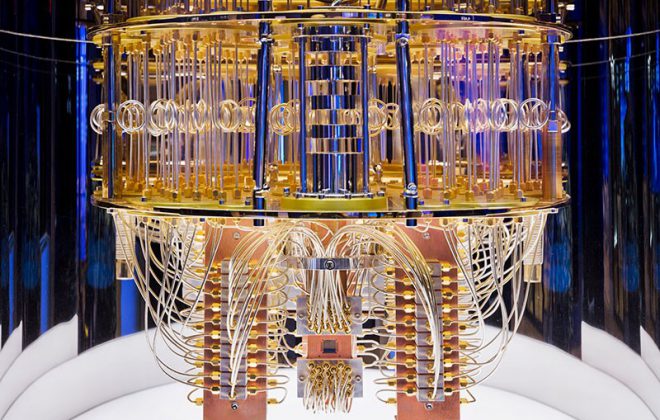
AI and Quantum Computing
When quantum computing arrives, it will allow AI to solve bigger problems and deal with an exponentially vaster quantity of data. Quantum computing is where instead of using the conventional 1s and 0s to represent data, it uses qubits, which can represent numerous 1s and 0s at the same time.
This fascinating phenomena allows the quantum computer to crunch through data more efficiently and at quicker speeds, thus making AI better.
AI already impacts our lives everyday, but as I’ve strived to mention time and time again, it has so much potential and a wide array of opportunities to continue to change the world.
Let’s just hope it doesn’t take over the world.
Sources:
- Milestones in artificial intelligence – ThinkAutomation. (2022). Retrieved 19 January 2022, from https://www.thinkautomation.com/histories/milestones-in-artificial-intelligence/
- Adams, R. (2022). 10 Powerful Examples Of Artificial Intelligence In Use Today. Retrieved 19 January 2022, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/robertadams/2017/01/10/10-powerful-examples-of-artificial-intelligence-in-use-today/?sh=28fd83f7420d
- AI is the biggest technological breakthrough of the 21st century - January 19, 2022
- 3D printing is the future of the construction industry - January 14, 2022
- The top 5 tech that caught my eye in CES 2022 - January 10, 2022